Getting Started with Okteto and Node.js
Okteto is a platform that simplifies the process of launching cloud development environments without requiring the expertise to do this yourself. This enables developers to automatically spin up fully-managed development environments that emulate production as closely as possible. Okteto eliminates the friction of local development environments, the many deviations that can exist for the same engineering organization, and the troubleshooting that comes with them.
This tutorial will show you how to develop and debug a Node.js application using Okteto.
Prerequisites
Install the latest version of the Okteto CLI and configure it to access Okteto. Follow our installation guide if you haven't done it yet.
Step 1: Deploy the Node.js Sample App
Get a local version of the Node.js Sample App by executing the following commands:
$ git clone https://github.com/okteto/node-getting-started
$ cd node-getting-started
At the root of the directory, you'll find the okteto.yml file. This file describes how to deploy the Node Sample App.
deploy:
- kubectl apply -f k8s.yml
Deploy your development environment by executing:
$ okteto deploy
i Using cindy @ okteto.example.com as context
i Running kubectl apply -f k8s.yml
deployment.apps/hello-world created
service/hello-world created
ingress.networking.k8s.io/hello-world created
✓ Development environment 'node-getting-started' successfully deployed
i Run 'okteto up' to activate your development container
Log into your Okteto instance and click on the URL of the application:
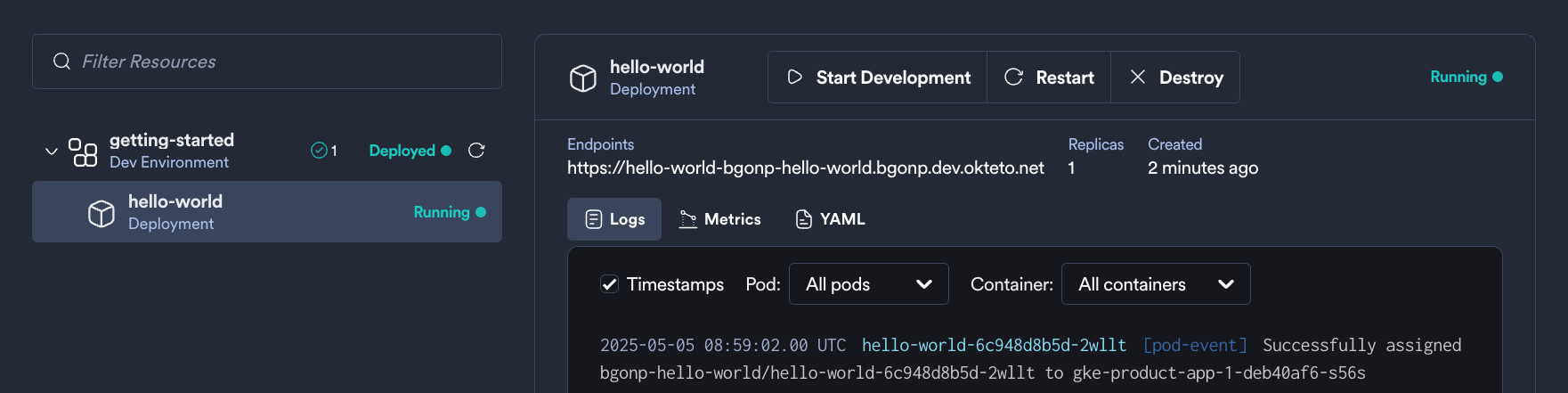
Did you notice that you're accessing your application through an HTTPs endpoint? This is because Okteto will automatically create them for you when you deploy your application. Cool no 😎?
Step 2: Activate your development container
The dev section defines how to activate a development container for the Node Sample App:
dev:
hello-world:
command: bash
sync:
- .:/usr/src/app
forward:
- 9229:9229
The hello-world key matches the name of the hello world Deployment. The meaning of the rest of fields is:
command: the start command of the development container.sync: the folders that will be synchronized between your local machine and the development container.forward: a list of ports to forward from your development container to localhost in your machine. This is needed to configure the Node remote debugger.
Also, note that there is a .stignore file to indicate which files shouldn't be synchronized to your development container.
This is useful to avoid synchronizing binaries, build artifacts, git metadata, or dependencies like the node_modules folder.
Next, execute the following command to activate your development container:
$ okteto up
✓ Persistent volume successfully attached
✓ Images successfully pulled
✓ Files synchronized
Namespace: cindy
Name: hello-world
Forward: 9229 -> 9229
Welcome to your development container. Happy coding!
cindy:hello-world app>
Working in your development container is the same as working on your local machine. Start the application in hot-reload mode by running the following command:
cindy:hello-world app> npm run start
> node-getting-started@1.0.0 start /usr/src/app
> nodemon index.js
[nodemon] 2.0.18
[nodemon] to restart at any time, enter `rs`
[nodemon] watching path(s): *.*
[nodemon] watching extensions: js,mjs,json
[nodemon] starting `node index.js`
Starting hello-world server...
Go back to the browser and reload the page to test that your application is running.
Step 3: Remote Development with Okteto
Open the index.js file in your favorite local IDE and modify the response message on line 5 to be Hello world from Okteto!. Save your changes.
res.send("Hello world from Okteto!");
Okteto will synchronize your changes to your development container.
Take a look at the development container shell and notice how the changes are detected by nodemon and automatically hot reloaded.
[nodemon] restarting due to changes...
[nodemon] starting `node index.js`
Starting hello-world server...
Go back to the browser and reload the page. Your code changes were instantly applied. No commit, build, or push required 😎!
Step 4: Remote debugging with Okteto
Okteto enables you to debug your applications directly from your favorite IDE. Let's take a look at how that works in VS Code, one of the most popular IDEs for Node development. If you haven't done it yet, install the Node.js extension available from Visual Studio marketplace.
Cancel the execution of nodemon index.js from the development container shell by pressing ctrl + c.
Rerun your application in debug mode:
cindy:hello-world app> npm run debug
Debugger listening on ws://0.0.0.0:9229/73d8d793-b0c3-4310-86ee-3a42938a5df1
For help, see: https://nodejs.org/en/docs/inspector
Open the Debug extension and run the Connect to okteto debug configuration (or press the F5 shortcut):
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Connect to okteto",
"type": "node",
"request": "attach",
"address": "localhost",
"port": 9229,
"localRoot": "${workspaceFolder}",
"remoteRoot": "/usr/src/app",
"skipFiles": ["<node_internals>/**"]
}
]
}
You should be replacing the value of remoteRoot with wherever your application code is.
Add a breakpoint on index.js, line 5. Go back to the browser and reload the page.
The execution will halt at your breakpoint. You can then inspect the request, the available variables, etc...
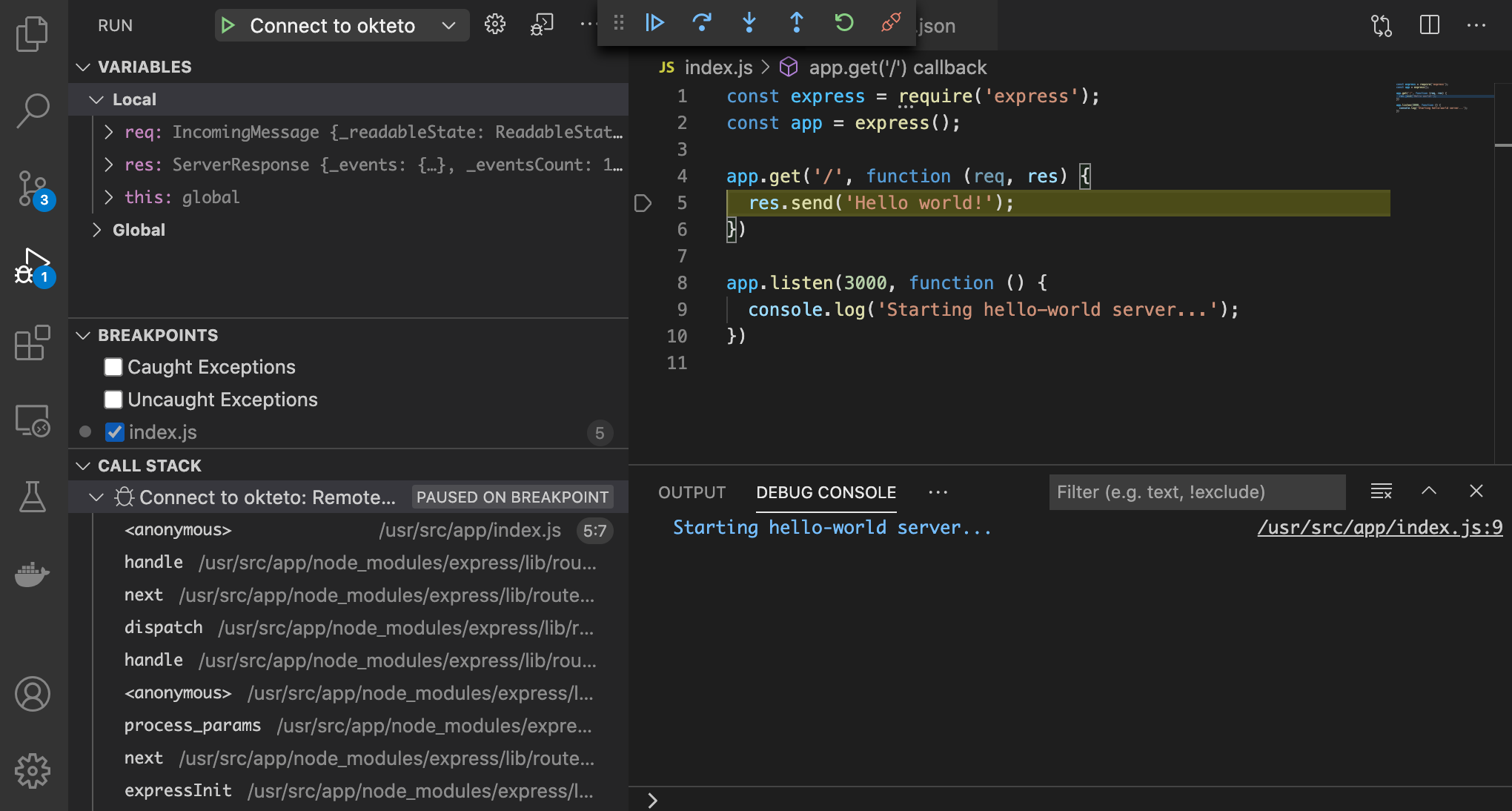
Your code is running in Okteto, but you can debug it from your local machine without any extra services or tools. Pretty cool no? 😉
Next steps
Congratulations, you just developed your first application in Okteto 🚀.
Okteto lets you develop your applications directly on Kubernetes. This way you can:
- Eliminate integration issues by developing in a realistic environment
- Test your application end to end as fast as you type code
- No more CPU cycles wasted in your machine. Develop at the speed of the cloud!
Find more advanced samples with Okteto in this repository or join our community to ask questions and share your feedback.