Remote Execution
The Okteto Manifest allows you to define a list of commands to deploy, test and destroy your application.
By default, your commands run locally in your machine, but we recommend that you enable remote execution.
Enable Remote Execution
You can enable remote execution by default for all applications or on a per application basis.
Enable Remote Execution by Default
Remote Execution can also be made the default by configuring it in the Admin Dashboard.
Navigate to Admin -> Command Line(CLI) under the Settings section to enable it.
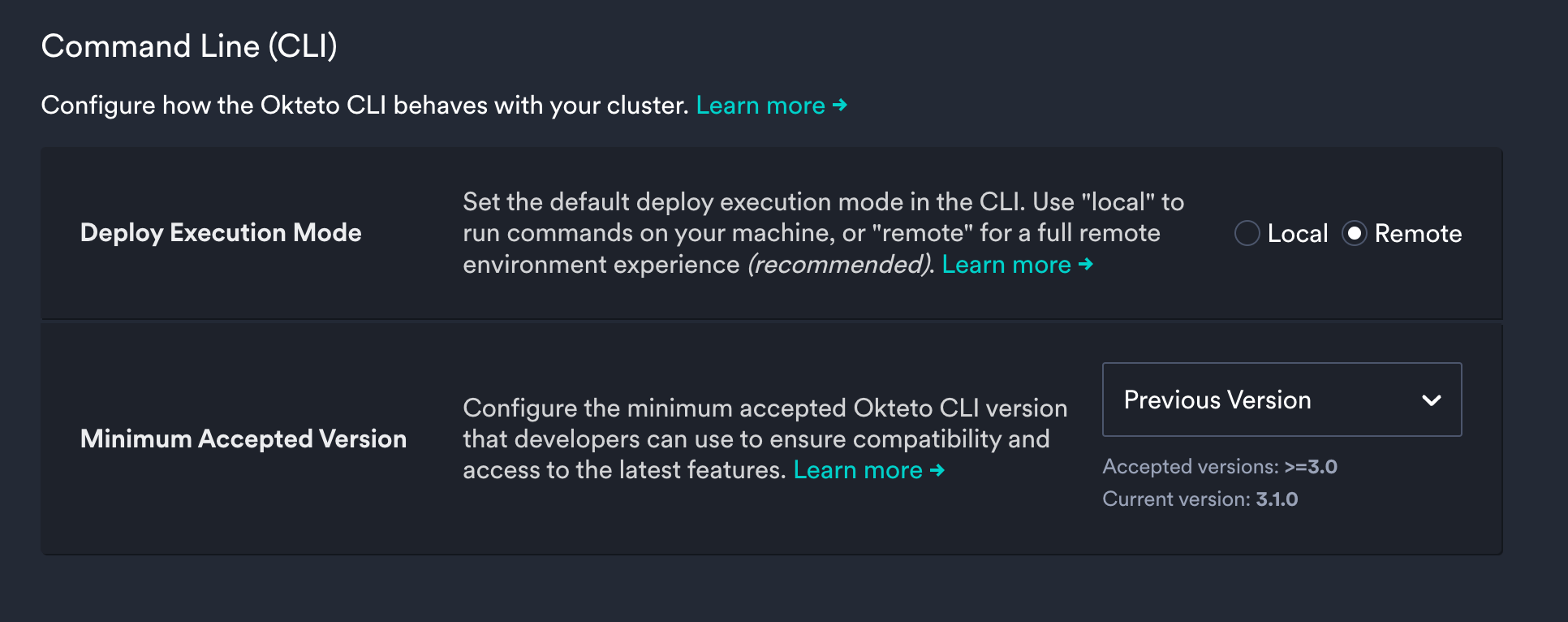
Local execution is deprecated. Okteto recommends that you enable remote execution for your deploy/destroy commands
Enable Remote Execution per Application
To use remote execution per application, you can enable it by setting the remote field to true in the deploy/destroy section of your Okteto Manifest:
deploy:
remote: true
commands:
- helm upgrade --install movies chart
Remote execution is always enabled for okteto test
By default, your commands will run in a remote container using our default container image in the workdir /okteto/src.
The default container image is a Debian Linux container with the following tools preinstalled:
bashcurlenvsubstgithelmkubectlkustomizemakeoktetoopensshwait-for-it
Remote execution means you don't have to worry about installing tools like helm, kubectl, and others on your local machine.
Defining Your Own Image
If you need custom tooling or advanced logic, you can use your own image for remote execution.
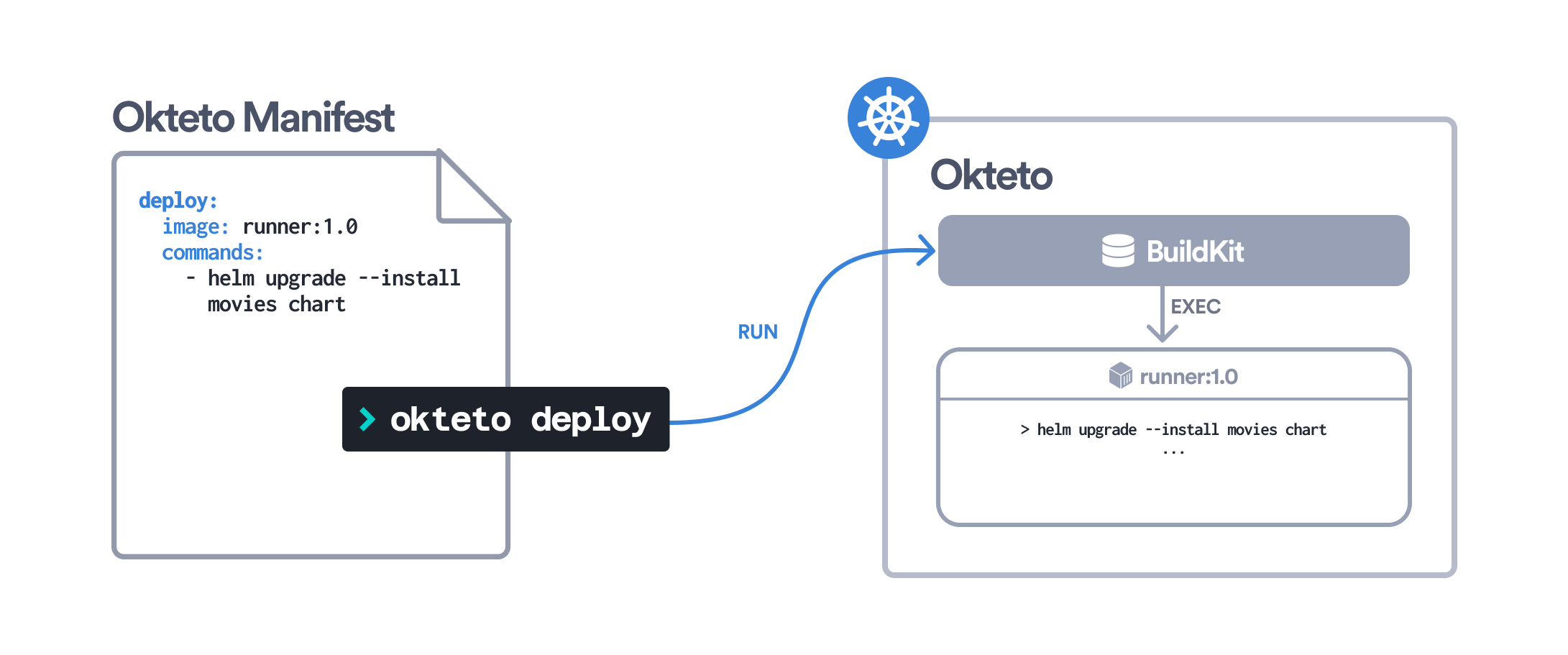
For example, if you want to use the image runner:1.0 as the runtime of your remote execution, configure your Okteto Manifest like this:
deploy:
image: runner:1.0
commands:
- helm upgrade --install movies chart
You can use your own image to force specific versions of your deployment tools and ensure that your team has a consistent experience when working with Okteto.
How Remote Execution Works
When running on remote, Okteto will automatically synchronize your local folder to a container running inside Buildkit:
Okteto mounts the Okteto SSH Key within the container running inside Buildkit. This allows you to clone any private git repository as part of your commands execution as long as the Okteto SSH Key has the appropriate access privileges.
Ignoring Files
By default, Okteto synchonizes all files in the folder where the Okteto Manifest is located to the container running inside Buildkit.
You can also configure the folder to be synchronized using the context field:
deploy:
image: runner:1.0
context: .
commands:
- helm upgrade --install movies chart
You can optimize which files are synchronized to the container running inside Buildkit by using a .oktetoignore file, located in the folder specified by the context field. If this file exists, the CLI will exclude from synchronization any files and directories that match patterns in it.
This helps avoid unnecessarily synchronizing large or sensitive files and directories that are not used by the commands defined in your Okteto Manifest.
An example .oktetoignore file would be the following:
# applied to all commands
docs
# applied to deploy commands only
[deploy]
integration/*
# applied to destroy commands only
[destroy]
app
# applied to all test commands
[test]
app
# applied to unit test command only
[test.unit]
integration
This .oktetoignore expands to the following rules:
- For deploys, ignores
docsandintegration/**. - For destroys, ignores
docsandapp. - For any test, ignores
docsandapp. - For the unit test specifically, ignores
docs,appandintegration.
Each command group in .oktetoignore uses the same format as .dockerignore files.
For remote deploy and destroy operations, Okteto also reads the legacy .oktetodeployignore file but it will be deprecated in future versions.